Kidney Stones Treatment in India: Comprehensive Guide for International Patients
Kidney Stones Treatment in India: Comprehensive Guide for International Patients
Kidney Stones Treatment in India
Understanding Kidney Stones
Kidney stones represent a common urological condition characterized by the formation of hard mineral and salt deposits within the kidneys. These crystalline formations can vary significantly in size, shape, and composition, affecting not just the kidneys but potentially any part of the urinary tract, including the ureters, bladder, and urethra.
Kidney Stone Formation and Composition
The process of kidney stone formation, known as nephrolithiasis, typically begins when certain substances in urine—such as calcium, oxalate, and phosphorus—become highly concentrated. In a more diluted urine, these substances are more likely to dissolve. However, when urine is concentrated, these substances can crystallize, initiating the formation of stones. Over time, these crystals can attract other elements, growing into solid masses, or stones, within the kidneys.
Kidney stones can comprise various materials, the most common being:
Calcium Stones: The most prevalent type of kidney stones, usually in the form of calcium oxalate. Oxalate is a substance found naturally in food, but the liver also produces it daily. Dietary factors, high doses of vitamin D, and certain metabolic disorders can increase the concentration of calcium or oxalate in urine, contributing to the formation of calcium stones.
Uric Acid Stones: These can form in individuals who lose too much fluid due to chronic dehydration, those who consume a high-protein diet, and those with gout. Certain genetic factors may also increase the risk of uric acid stones.
Struvite Stones: These stones are often associated with urinary tract infections. They can grow quickly and become quite large, sometimes with few symptoms or warning signs.
Cystine Stones: Representing a more rare type, cystine stones result from a hereditary disorder called cystinuria, which affects the amount of acid that the kidney excretes.
Factors Influencing Stone Formation
Several factors can influence the likelihood of developing kidney stones, including:
Fluid Intake: Low fluid intake and, consequently, low urine volume can lead to higher urine concentration, increasing the risk of stone formation.
Diet: A diet high in protein, sodium, and sugar can promote the formation of certain types of kidney stones, particularly in individuals with a predisposition to the condition.
Body Weight: Obesity may increase the risk of kidney stones due to changes in acid levels in the urine and the physical stress obesity places on the kidneys.
Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as renal tubular acidosis, hyperparathyroidism, and urinary tract infections, can contribute to specific types of kidney stones.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Environmental factors, including geographical location and seasonal changes, can also affect the risk of kidney stone formation. Regions with hotter climates tend to have higher rates of kidney stone prevalence due to increased fluid loss through sweat and the resultant concentrated urine. Lifestyle factors, including sedentary behavior and inadequate water intake, further compound this risk.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones may not cause symptoms until they move within the kidney or pass into the ureter, the tube connecting the kidney and bladder. When this happens, notable symptoms can include:
Severe Pain: The hallmark symptom of kidney stones is intense pain, known as renal colic, which can start in the side or back, below the ribs, and may spread to the lower abdomen and groin. The pain often comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity.
Pain During Urination: When a stone reaches the junction between the ureter and bladder, individuals may experience pain during urination.
Discolored Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can cause the urine to appear pink, red, or brown, signaling the presence of a kidney stone.
Frequent Urination: An increased need to urinate, often accompanied by an urgency that doesn't correlate with the volume of urine released.
Nausea and Vomiting: The severe pain associated with kidney stones can lead to nausea or vomiting.
Diagnosis of Kidney Stones
Diagnosing kidney stones typically involves a combination of clinical assessment and diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of stones and determine their size, location, and composition.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A healthcare provider will review the patient's medical history for any risk factors or previous occurrences of kidney stones and conduct a physical examination. This may include palpating the abdomen and back for any signs of tenderness.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can check for high levels of minerals involved in stone formation, such as calcium, and assess kidney function. Elevated levels of certain substances in the blood can indicate the presence of stones.
Urine Testing
A 24-hour urine collection test may be conducted to find any abnormal excretion of minerals that could promote stone formation. This test can also detect a lack of substances that help prevent crystallization.
Imaging Tests
Imaging studies are crucial for locating and characterizing kidney stones:
CT Scans: Non-contrast helical CT scans are the most effective imaging test for kidney stones, providing detailed images that help identify even small stones throughout the urinary tract.
Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that can detect stones and assess for any obstruction or swelling in the kidneys or ureter.
X-rays: While less detailed than CT scans, X-rays can still identify many types of kidney stones and are used in certain situations.
Specialized Tests
In some cases, additional diagnostic procedures may be needed:
Urodynamic Testing: Although not commonly used for diagnosing kidney stones, these tests can assess how well the urinary tract is storing and releasing urine, especially in patients with recurrent stones or other urinary issues.
Biopsy: Rarely, a biopsy may be performed during a ureteroscopy if a stone or the tissue around it appears unusual, to rule out other conditions.
Understanding the symptoms and diagnosis of kidney stones is crucial for timely and effective treatment, which can significantly alleviate pain and prevent complications.
Treatment Options in India for Kidney Stones
India's healthcare landscape is renowned for its comprehensive and advanced medical treatments for kidney stones, making it a preferred destination for patients seeking high-quality care. The country offers a range of effective treatments, including cutting-edge, minimally invasive procedures that prioritize patient comfort and swift recovery.
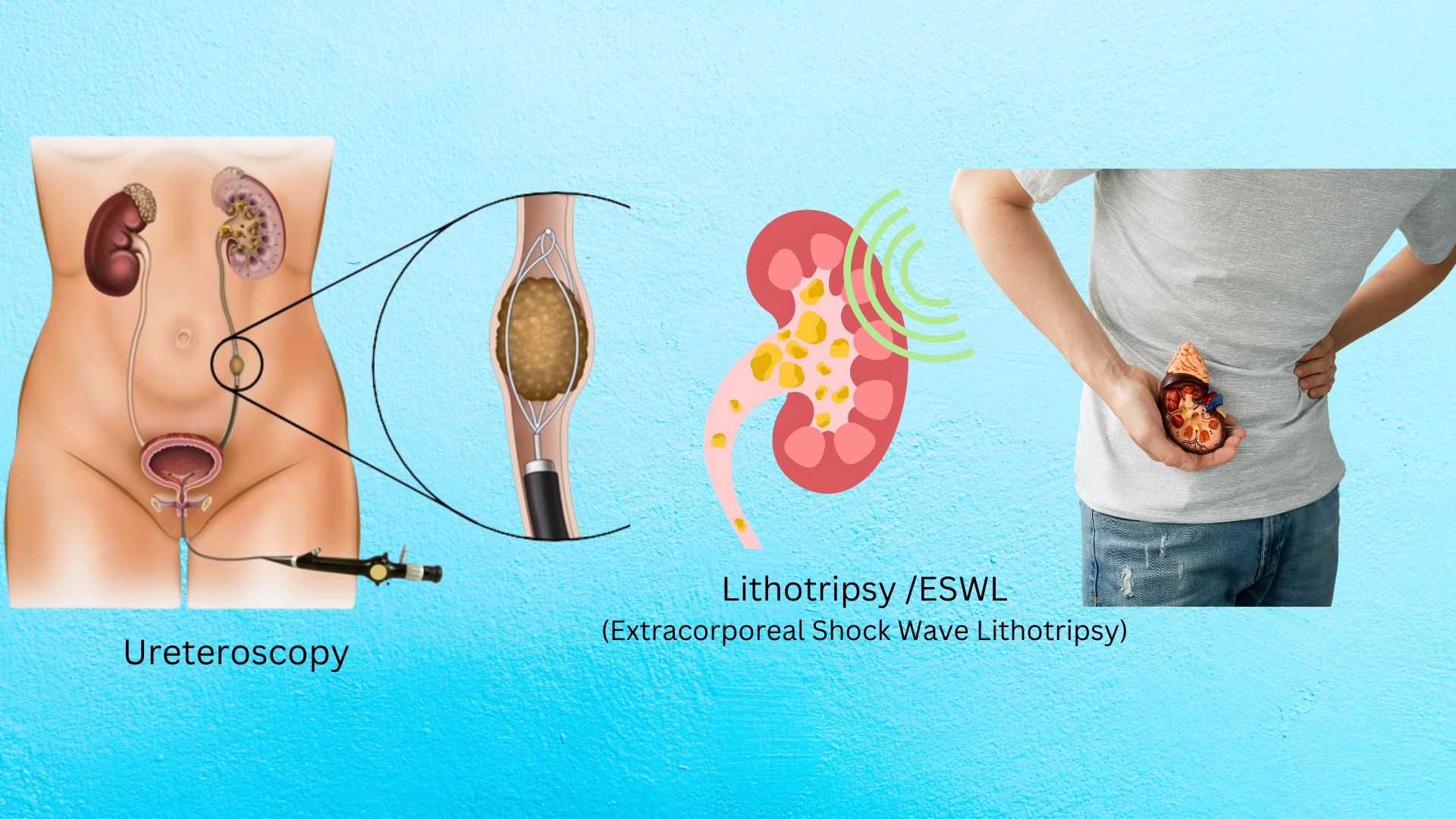
Lithotripsy (Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy, ESWL)
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) stands out as a preferred non-invasive treatment option for kidney stones. This procedure utilizes high-energy shock waves to target and break down kidney stones into smaller fragments. These fragments are then naturally passed through the urinary tract with urine. ESWL is particularly effective for stones that are less than 2 cm in diameter and located within the kidney.
Ureteroscopy
Ureteroscopy is a minimally invasive technique designed for the removal or fragmentation of stones in the ureter or kidney. A thin, flexible scope is inserted through the urethra and bladder, reaching the stones, which are then either extracted intact or broken down using a laser. This method is highly effective for stones located in the ureter and lower kidney, offering a high success rate with minimal complications.
Treatment Procedures and Recovery
Pre-Treatment Evaluation
A thorough pre-treatment evaluation is crucial to determining the most appropriate treatment strategy. Detailed imaging studies, such as ultrasound, X-ray, or CT scans, are conducted to ascertain the size, number, and location of the kidney stones. This information helps in selecting the most suitable treatment modality.
Surgical Treatment
Lithotripsy: ESWL is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, allowing patients to return home the same day. The process requires minimal preparation, and recovery time is short, with patients resuming normal activities shortly after the procedure.
Ureteroscopy: This procedure may necessitate a brief hospital stay, often not exceeding one or two days. Recovery is generally quick, with most patients able to resume their regular activities within a couple of days post-procedure.
Post-Surgery Care
Post-operative care is focused on managing any discomfort, ensuring adequate hydration to facilitate the passage of stone fragments, and monitoring for the complete clearance of stones. Patients are usually advised to increase their fluid intake to help flush out the stone fragments more efficiently.
Rehabilitation
While specific rehabilitation may not be required following kidney stone treatment, patients are often counseled on dietary and lifestyle modifications to minimize the risk of recurrent stone formation. This includes advice on hydration, dietary salt intake, and the consumption of certain foods that may influence stone formation.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments play a critical role in ensuring the successful outcome of the treatment. These appointments may include imaging tests to confirm that all stone fragments have been passed and discussions on preventive measures to reduce the risk of future stone formation.
India has emerged as a premier destination for patients from around the globe seeking advanced and cost-effective medical treatments, particularly for conditions like kidney stones. The country's healthcare system combines state-of-the-art technology with a patient-centered approach, ensuring both high success rates and a positive experience for international patients.
Estimated Stay Duration for International Patients in India
Hospital Stay (IPD)
Depending on the chosen treatment method for kidney stones, the hospital stay can range from not required at all to approximately 1-2 days. For instance, patients undergoing Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) may not need to stay overnight, while those having ureteroscopy might need a short hospitalization to ensure proper post-operative recovery.
Total Stay in India (OPD)
International patients should anticipate a total stay of about 1-2 weeks in India. This duration allows for a comprehensive approach to care, encompassing pre-operative assessments, the treatment procedure itself, and a period of initial recovery under medical supervision. This timeline ensures that patients are adequately prepared for their procedure and begin their recuperation with the necessary healthcare support.
Treatment Success Rate
Both lithotripsy and ureteroscopy boast high success rates in the treatment of kidney stones within the Indian healthcare landscape. These procedures are effective in not only removing stones but also in significantly reducing the recurrence of symptoms, with minimal risk of complications. The expertise of Indian urologists and the use of advanced medical technologies contribute to these favorable outcomes.
Treatment Cost in USD
Lithotripsy: The cost for lithotripsy in India typically ranges from approximately $1,500 to $3,000. This variation in cost can depend on the complexity of the case, the specific technology used, and the facility chosen.
Ureteroscopy: The cost for ureteroscopy is slightly higher, ranging from approximately $2,000 to $4,000. Similar to lithotripsy, the cost can vary based on the surgical approach, the hospital's pricing policy, and any additional interventions that may be required.
These costs are indicative and offer international patients affordable options compared to the costs of similar treatments in many Western countries.
Final Thoughts
India's healthcare system is well-prepared to offer effective and efficient treatments for kidney stones, leveraging the latest in medical technology and the expertise of skilled specialists. International patients opting for treatment in India can look forward to receiving high-quality care tailored to their specific needs, ensuring a successful treatment outcome and an enhanced quality of life post-recovery.
Disclaimer
This overview serves educational purposes only and should not be seen as a substitute for professional medical advice. Prospective patients are encouraged to consult with healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and a treatment plan that is specifically tailored to their health condition. It's important to note that treatment costs and outcomes can vary significantly based on individual patient factors and circumstances.
No doctors found for this treatment.
No hospitals found for this treatment.

